Volume 562 Issue 7726, 11 October 2018
2018年10月11日,第562卷第7726期

生物科学Bio-Science
Common genetic variants contribute to risk of rare severe neurodevelopmental disorders
常见遗传变异增加罕见严重神经发育障碍风险
作者:Mari E. K. Niemi, Hilary C. Martin, Daniel L. Rice, Giuseppe Gallone, et al.
相关链接:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-018-0566-4
导读:
具有相同遗传缺陷的患者可能有不同的临床表现,一些携带已知致病变异基因的患者可能看起来似乎并未受到影响。
为了理解这些差异的原因,作者研究了6987名儿童构成的同生群,他们被临床遗传学家诊断为患有严重的神经发育障碍,同时经常伴有其他器官系统异常。
虽然这些神经发育障碍的遗传原因预计几乎完全是单基因的,但研究者发现7.7%的风险变异可归因于继承性的共同遗传变异。
研究者发现,个体之间是否有一种已知蛋白编码诊断变异,其共有变异风险并没有显著差异,这表明共有变异风险会影响有和没有单基因诊断的患者。
此外,此前发表的自闭症、身高、出生体重和颅内容积的共同变异情况均与此次研究同生群的这些特征相关,表明单基因障碍患者的表型表达受到与普通人群相同变异的影响。
研究结果表明,常见的遗传变异既影响总体风险,也影响通常被认为是单基因的神经发育障碍的临床表现。
Abstract:Patients with the same genetic defect can have different clinical presentations, and some individuals who carry known disease-causing variants can appear unaffected. Here, to understand what explains these differences, we study a cohort of 6,987 children assessed by clinical geneticists to have severe neurodevelopmental disorders, often in combination with abnormalities of other organ systems. Although the genetic causes of these neurodevelopmental disorders are expected to be almost entirely monogenic, we show that 7.7% of variance in risk is attributable to inherited common genetic variation. We found that common-variant risk was not significantly different between individuals with and without a known protein-coding diagnostic variant, which suggests that common-variant risk affects patients both with and without a monogenic diagnosis. In addition, previously published common-variant scores for autism, height, birth weight and intracranial volume were all correlated with these traits within our cohort, which suggests that phenotypic expression in individuals with monogenic disorders is affected by the same variants as in the general population. Our results demonstrate that common genetic variation affects both overall risk and clinical presentation in neurodevelopmental disorders that are typically considered to be monogenic.
Principles of nucleosome organization revealed by single-cell micrococcal nuclease sequencing
单细胞微球菌核酸酶测序揭示核小体组织原理
作者:Binbin Lai, Weiwu Gao, Kairong Cui, Wanli Xie, et al.
相关链接:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-018-0567-3
导读:
即使在同源的细胞群中,细胞在响应活跃的信号时也表现出异质性,这可能与染色质可及性的异质性有关。
研究人员报告了一种叫作单细胞微球菌核酸酶测序(scmnas -seq)的技术,可用于同时测量单个细胞中的全基因组核小体定位和染色质可及性。
研究者发现了脱氧核糖核酸酶I(DNase I)超敏位点核小体间隔的双峰分布,该分布与不可及和可及状态相对应,并且与核小体变异和细胞间可及性的变异有关。
核小体变异在单个细胞中比跨细胞更少,在同一细胞类型中比跨细胞类型更少。
大量的原始CD4 T细胞和小鼠胚胎干细胞显示,在其各自分化谱系中检测到的新生增强子中,核糖体的占用减少,这表明在未分化的细胞群中,存在着准备分化为特定谱系的细胞。
Abstract:Even in a homogenous population of cells, cells exhibit heterogeneity in expression in response to active signalling that may be related to heterogeneity in chromatin accessibility. Here we report a technique, termed single-cell micrococcal nuclease sequencing (scMNase-seq), that can be used to simultaneously measure genome-wide nucleosome positioning and chromatin accessibility in single cells. We found a bimodal distribution of nucleosome spacing at DNase I hypersensitive sites, which corresponds to inaccessible and accessible states and is associated with nucleosome variation and variation in accessibility across cells. Nucleosome variation is smaller within single cells than across cells, and smaller within the same cell type than across cell types. A large fraction of naive CD4 T cells and mouse embryonic stem cells shows depleted nucleosome occupancy at the de novo enhancers detected in their respective differentiated lineages, revealing the existence of cells primed for differentiation to specific lineages in undifferentiated cell populations.
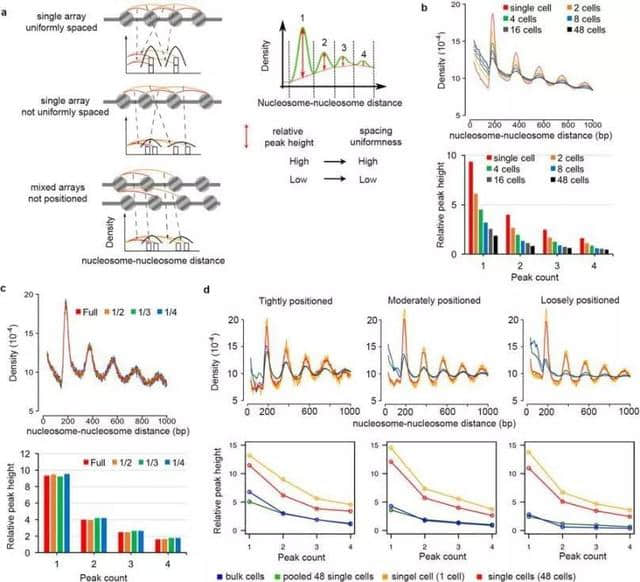
Extended Data Fig. 3: Measuring uniformity in nucleosome spacing in single cells. 测量单个细胞内核小体间距均匀性
电子学Electronic
Electronic noise due to temperature differences in atomic-scale junctions
由原子尺度结点温差产生的电子噪声
作者:Ofir Shein Lumbroso, Lena Simine, Abraham Nitzan, Dvira Segal & Oren Tal
相关链接:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-018-0592-2
导读:
自一个世纪前发现电子热噪声和散射噪声以来,这些基本噪声形式对科学技术的研究和应用产生了巨大的影响。
研究者报告了对一种基本电子噪声的测量,该噪声是由纳米级导体之间的温差产生的,研究者称之为“delta-T 噪声”。
研究结果表明,delta-T噪声不同于热噪声和电压激活的散射噪声。与热噪声一样,delta-T噪声也有纯热源,但它只有在不平衡的情况下才会产生。
delta-T噪声和标准散射噪声具有相同的划分起源,但却是被不同的刺激因素激活的。研究者推断,delta-T噪声可与热噪声结合,用于检测纳米导体之间的温差,而不需要制造精密的局部探针。
因此,它可以极大地促进纳米尺度的热传输研究。
Abstract: Since the discovery a century ago of electronic thermal noise and shot noise, these forms of fundamental noise have had an enormous impact on science and technology research and applications. Here we report measurements of a fundamental electronic noise that is generated by temperature differences across nanoscale conductors, which we term ‘delta-T noise’. Our findings show that delta-T noise is distinct from thermal noise and voltage-activated shot noise. Like thermal noise, it has a purely thermal origin, but delta-T noise is generated only out of equilibrium. Delta-T noise and standard shot noise have the same partition origin, but are activated by different stimuli. We infer that delta-T noise in combination with thermal noise can be used to detect temperature differences across nanoscale conductors without the need to fabricate sophisticated local probes. Thus it can greatly facilitate the study of heat transport at the nanoscale.
Solution-processable 2D semiconductors for high-performance large-area electronics
用于高性能大面积电子产品的可溶液旋涂二维半导体
作者:Zhaoyang Lin, Yuan Liu, Udayabagya Halim, Mengning Ding, et al.
相关链接:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-018-0574-4
导读:
制备高质量的可溶液旋涂二维半导体纳米片仍然是一个挑战。
研究者报告了一种制备高度均匀的、可溶液旋涂的相纯半导体纳米片的通用方法,该方法包括将季铵盐分子电化学插入到二维晶体中,然后进行温和的声波降解和剥离过程。
通过对插层化学的精确控制,得到了薄相纯半导体2H-MoS2纳米片。
然后,这些纳米片被进一步加工成高性能薄膜晶体管,在室温下,其移动速度约为10平方厘米每伏特每秒,开/关比为106,大大超过以往溶液旋涂的MoS2薄膜晶体管。
大型薄膜晶体管阵列的大规模制造使得功能逻辑闸和计算电路的构建成为可能。
Abstract:Preparing high-quality solution-processable 2D semiconductor nanosheets remains a challenge. We report a general approach to preparing highly uniform, solution-processable, phase-pure semiconducting nanosheets, which involves the electrochemical intercalation of quaternary ammonium molecules into 2D crystals, followed by a mild sonication and exfoliation process. By precisely controlling the intercalation chemistry, we obtained phase-pure, semiconducting 2H-MoS2 nanosheets with a narrow thickness distribution. These nanosheets were then further processed into high-performance thin-film transistors, with room-temperature mobilities of about 10 square centimetres per volt per second and on/off ratios of 106 that greatly exceed those obtained for previous solution-processed MoS2 thin-film transistors. The scalable fabrication of large-area arrays of thin-film transistors enabled the construction of functional logic gates and computational circuits.
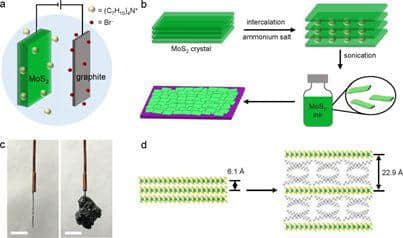
Extended Data Fig. 1: Molecular intercalation and exfoliation of MoS2 nanosheets. MoS2纳米片的分子插入和剥落
天体物理学Astrophysics
An evolving jet from a strongly magnetized accreting X-ray pulsar
来自强磁化吸积X射线脉冲星的演变性喷流
作者:J. van den Eijnden, N. Degenaar, T. D. Russell, R. Wijnands, et al.
相关链接:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-018-0524-1#Sec13
导读:
相对论性喷流在整个宇宙中都可以观察到,并在从双星系统到星系和星系团的物理尺度范围内强烈地影响着它们周围的环境。
研究人员报告了由强磁化中子星发射的不断演化的喷流的观测结果,该喷流的吸积速率超过了爱丁顿极限给出的理论最高速率。
其射电光度比其他具有类似X射线发光强度的中子星微弱两个数量级,这意味着中子星的性质在调节射流强度方面具有重要作用。
研究结果还表明,超亮X射线脉冲星的强磁场并不能阻止这些源头发射喷流。
Abstract: Relativistic jets are observed throughout the Universe and strongly affect their surrounding environments on a range of physical scales, from Galactic binary systems1 to galaxies and clusters of galaxies. Here we report observations of an evolving jet launched by a strongly magnetized neutron star accreting above the theoretical maximum rate given by the Eddington limit. The radio luminosity of the jet is two orders of magnitude fainter than those seen in other neutron stars with similar X-ray luminosities9, implying an important role for the properties of the neutron star in regulating jet power. Our result also shows that the strong magnetic fields of ultra-luminous X-ray pulsars do not prevent such sources from launching jets.

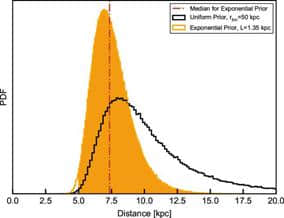
Fig. 1: Marginal posterior distributions for the distance to Sw J0243. 到Sw J0243距离的边际后验分布。
Nearly all the sky is covered by Lyman-α emission around high-redshift galaxies
几乎所有天空覆盖着高红移星系周围的莱曼-α放射
作者:L. Wisotzki, R. Bacon, J. Brinchmann, S. Cantalupo, P. Richter, et al.
相关链接:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-018-0564-6
导读:
通过莱曼-α放射跟踪宇宙中的氢是观测天体物理学的一个长期目标,但这种广泛延伸的发射的表面亮度却极低,从而形成了难以逾越的障碍。
近日,来自高红移星系周围氢无处不在的莱曼-α放射的发现为观察周围的星系环境打开了一个新窗口。这种测量以前仅限于特别有利的天体系统,或是由于该放射很微弱而要使用大量统计进行平均。
此次,研究者报告在3至6等微弱星系红移周围观察到低表面亮度的莱曼-α放射。他们发现,天空投射覆盖率接近100%。
相应的入射率(由任意视线洞察的莱曼-α放射极的平均数量)远高于整体,并且类似于高密度吸收体经常在遥远的类星体光谱中探测到的入射率。
这种相似性表明,这些红移星系周围的大多数氢原子已经在发射中被探测到。
Abstract: Tracing cosmic hydrogen through its Lyman-α emission has been a long-standing goal of observational astrophysics, but the extremely low surface brightness of the spatially extended emission is a formidable obstacle. A new window into circumgalactic environments was recently opened by the discovery of ubiquitous extended Lyman-α emission from hydrogen around high-redshift galaxies. Such measurements were previously limited to especially favourable systems or to the use of massive statistical averaging because of the faintness of this emission. Here we report observations of low-surface-brightness Lyman-αemission surrounding faint galaxies at redshifts between 3 and 6. We find that the projected sky coverage approaches 100 per cent. The corresponding rate of incidence (the mean number of Lyman-α emitters penetrated by any arbitrary line of sight) is well above unity and similar to the incidence rate of high-column-density absorbers frequently detected in the spectra of distant quasars. This similarity suggests that most circumgalactic atomic hydrogen at these redshifts has now been detected in emission.
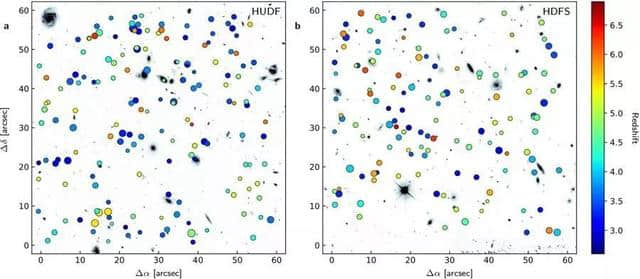
Extended Data Fig. 1: Spatial distribution and redshifts of the Lyα emitter sample.
莱曼-α放射体样本的空间分布和红移。
气候Climate
Trade-offs in using European forests to meet climate objectives
对利用欧洲森林实现气候目标的权衡
作者:Sebastiaan Luyssaert, Guillaume Marie, Aude Valade, Yi-Ying Chen,et al.
相关链接:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-018-0577-1
导读:
欧洲提出的可持续森林管理的投资组合是否符合巴黎协议尚待确认,也就是说尚不能确定该组合能否降低大气中CO2的增长速度、减少大气层顶部辐射的失衡,以及在21世纪结束时,既不会增加近地表气温也不会减少降水。
这项研究展示了由管理系统组成的投资组合通过碳封存、木材使用、产品和能源替代等办法在局部地区让碳汇最大化,降低了局地大气CO2的增长率,但并未满足任何其他标准。
研究结果表明,如果目前的森林覆盖能够持续下去,通过森林管理获得的额外气候效益将是有限的、局部的,而非全球性的。
基于此,研究者认为欧洲不应该依赖森林管理缓解气候变化。
Abstract:It remains to be confirmed whether commonly proposed sustainable European forest-management portfolios would comply with the Paris Agreement—that is, whether they can reduce the growth rate of atmospheric CO2, reduce the radiative imbalance at the top of the atmosphere, and neither increase the near-surface air temperature nor decrease precipitation by the end of the twenty-first century. Here we show that the portfolio made up of management systems that locally maximize the carbon sink through carbon sequestration, wood use and product and energy substitution reduces the growth rate of atmospheric CO2, but does not meet any of the other criteria. Our results demonstrate that if present-day forest cover is sustained, the additional climate benefits achieved through forest management would be modest and local, rather than global. On the basis of these findings, we argue that Europe should not rely on forest management to mitigate climate change.
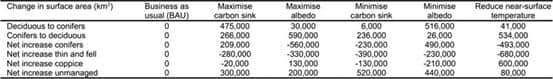
Extended Data Table 1 Changes in surface area of European forests by 2100 for six different forest-management portfolios. 到2100年,用于6个不同的森林管理组合的欧洲森林面积的变化。
Effects of climate warming on photosynthesis in boreal tree species depend on soil moisture
气候变暖对北方树种光合作用的影响取决于土壤水分
作者:Peter B. Reich, Kerrie M. Sendall, Artur Stefanski, et al.
相关链接:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-018-0582-4
导读:
气候变暖会通过热效应以及改变土壤湿度影响光合作用。这两种效应对全球森林广大区域来说都可能很重要。
研究展示了随着生长季节从雨季过渡到适度干旱期,气候变暖对南北方树种从积极到消极的影响。
在对11种温带和北方幼林的进行为期3年的露天增温实验中,当气温升高3.4℃时,最湿润土壤中的光饱和净光合作用和叶片扩散电导平均在1/3的时间里增加了。
而在干旱期,所有11种植物的叶片扩散电导以及光饱和净光合作用均下降了,而且温度升高的植物中的相关下降幅度比在常温下的植物大得多。因此,在干旱土壤中,温度升高在2/3的时间里减少了光饱和净光合作用。
由此可见,低土壤湿度可能会降低,甚至逆转气候变暖在湿度适中、季节性寒冷环境下光合作用的潜在益处,而且在生长季节期间的干旱期和经常发生湿度干旱期均会如此。
Abstract:Climate warming will influence photosynthesis via thermal effects and by altering soil moisture. Both effects may be important for the vast areas of global forests. Here we show that the effects of climate warming flip from positive to negative as southern boreal forests transition from rainy to modestly dry periods during the growing season. In a three-year open-air warming experiment with juveniles of 11 temperate and boreal tree species, an increase of 3.4 °C in temperature increased light-saturated net photosynthesis and leaf diffusive conductance on average on the one-third of days with the wettest soils. In all 11 species, leaf diffusive conductance and, as a result, light-saturated net photosynthesis decreased during dry spells, and did so more sharply in warmed plants than in plants at ambient temperatures. Consequently, across the 11 species, warming reduced light-saturated net photosynthesis on the two-thirds of days with driest soils. Thus, low soil moisture may reduce, or even reverse, the potential benefits of climate warming on photosynthesis in mesic, seasonally cold environments, both during drought and in regularly occurring, modestly dry periods during the growing season.
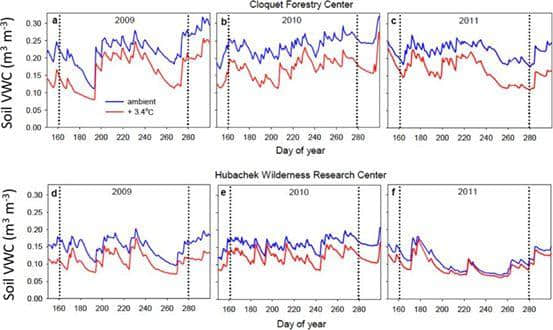
Fig. 1 Soil water (VWC) in relation to day of year. 土壤水分(VWC)与时间的关联。
(晋楠)
注意!微信又双叒叕更新了......
此次改版后,每个用户最多可以设置12个常读订阅号,这些订阅号将以往常的大图封面展示。为了不错过科学网的推送,请根据以下操作,将我们“星标”吧!
点击“科学网”进入公号页面→点击右上角的 ··· 菜单 →选择“设为星标”,搞定!



关注我们
微信号:sciencenet-cas(←长按复制) 或长按下方二维码